Greg Day
Greg Day is an artist, activist and cultural equity advocate. The camera has been an integral part of his journey in America and Europe for over half a century.
As a photographer and cultural anthropologist, Day has documented some of the most important cultural milieus and events of our time, including: The Civil Rights and Anti-War Movements in the South, early genderqueer performance artists and Greenwich Village luminaries in New York, African American life on the Gullah/Geechee Coast, the LGBT Rights Movement, California's cultural diversity and activism and Berlin's new architecture and queer art scene.
Greg: I am an artist, activist and cultural equity advocate. The camera has been an integral part of my journey in America and Europe for over half a century. As an artist and cultural anthropologist, I have documented some of the most important cultural milieus and events of our time, including: The Civil Rights and Anti-War Movements in the South, genderqueer performance artists and Greenwich Village luminaries in New York, African American life on the Gullah/Geechee Coast, the LGBT Rights Movement, California's cultural diversity and activism and Berlin's new architecture and Queer art scene.

Civil Rights Image © Greg Day
B&A: After we cover that amazing history we’ll move on to how you ended up in San Francisco and what you did here. How did you grow up? You became a social justice warrior and a very political artist. Were your parents Unitarian or Quaker or something like that?
GD: No, my mother was a secretary from Wisconsin and my father became an attorney from Alabama. They met in Washington D.C. under F.D.R.'s national job program where the government allocated a certain number of federal jobs for each state. My mother won the lottery in Madison, WI and went to Washington D.C.. My parents were not religious. My father was agnostic and my mother was raised Catholic, but hated it. When I came out to my mother, I was in my twenties and she said, “I knew you were gay since you were 4 years old. I don't care if you're gay. Just don't let the neighbors know.” I said, “What did you think when I married Kate Young, my former wife?” She said, “We thought that was really nice.”
I have a Polish immigrant grandfather who hated Poland and the Catholic Church. He married the daughter of German and Polish immigrants in Milwaukee. I come from a family of very outspoken adventurous, outside the box people, who are difficult and argumentative about their rights. My father taught me how to cross barriers. My grandfather was a carpenter and country school teacher. He and my father were workers on the first dam that F.D.R. built in the Tennessee Valley, the Joe Wheeler Dam. Vera Mahala Armstrong, my grandmother, was a descendant of survivors of the Trail of Tears. They were from Alabama so I spent my childhood there. Then my father’s career led him to Washington. We moved there between my junior and senior years of high school. I graduated from high school in Silver Springs, MD.
My father's family in Alabama was mixed race, although they passed as white. They were Native American, Appalachian, outsider people. My dad was outspoken and he raised me to be that way. My parents supported my being an artist from an early age,
In the late 1960s and early 1970s, I was an anthropology and photography student at Georgia State University in downtown Atlanta. Atlanta was a whirlwind of student activism, anti-war protests, civil rights marches. Dr. King's Southern Leadership Conference organization was located there. I went to a lot of demonstrations. I used photography to be a part of these activities and to document them. I wanted to make photographs like Dorothea Lange, documentary photography with a social justice agenda. I took the first course in African American culture offered there, by folklorist Mary Arnold Twining. She had completed field research on the Sea Islands of Georgia and South Carolina and took us there on field trips.

Basketmaker Mary Jane Manigault at her home in Hamlin Beach, SC, 1974.© Greg Day
On these field trips we went to the Gullah Geechee Coast’s basket-making community. On Highway I7, I met Mary Jane Manigault, the community’s matriarch and cultural broker. She was a very well-known basket-maker. I asked if I could take her picture, which is standard there— you buy a basket and then you can take a picture of the basket-maker. She said, “sure, go ahead”, and when I put the camera up to my eye she said, “I know what you're doing with that camera.” I put the camera down. I thought I had offended her. I said, “what do you mean?” She said, “you're waiting for your mind to turn on it.” “When you start out on a basket, you think you're gonna make a certain type, and while you're making it, suddenly the wall of the basket has turned in another direction, so I let my mind go with it. I never know what kind of basket I'm going to get until the end. But I know it's going to be great because I'm following my good mind.” She used her intuition, and that helped her become one of the most famous basket-makers in the United States. She was invited to the White House, and received a grant from the NEH. She was really extraordinary. Besides the basket-makers, I met African-American women quilters and the visionary artist Nellie Mae Rowe.
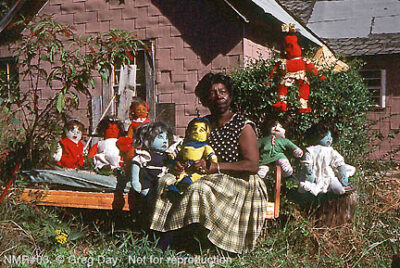
Mrs. Nellie Mae Rowe with her 'doll children'. Vinings, Georgia, 1978. © Greg Day
The Mt. Pleasant basket-makers make many things by hand, yet they are very contemporary. In this community everyone is involved in art production. Their process of making art is in the moment, improvisational, spontaneous, and without a lot of planning. They rely on dreams and being present in the moment These are the same principles that show up in every aspect of their life; what they were gonna wear in the morning; who they're gonna be... They changed my entire conception and practice of photography: their art process and their way of dealing with the world became mine.
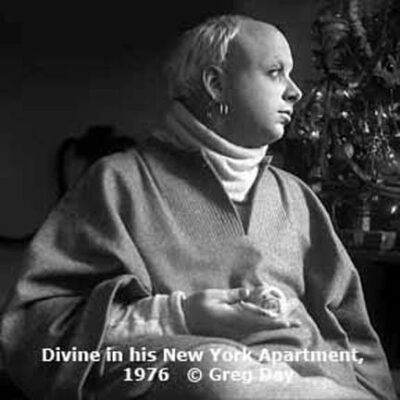
Kate Young and I were both accepted in Rutgers University's Anthropology Graduate program. After we finished our coursework, we moved to Manhattan and lived in Greenwich Village. The city was bankrupt and rent was cheap. In the Village and Chelsea. I discovered a full-blown, underground queer art scene— writers, actors, performance artists — in the streets, clubs and on the piers. Here I met Stephen Varble, Ruth Truth, and Warhol Factory stars, Taylor Mead, Jackie Curtis and Mario Mondelli, The Hot Peaches performance group, Agosto Machado, playwright Doric Wilson, performance pioneer Jack Smith, and Divine. Once again, my camera provided access and I began to document the LGBTQ+ community.
In 1978, I moved to San Francisco as part of a Rainbow Migration that brought thousands of Queers to San Francisco and California. I had a teaching job lined up at San Francisco State. When I arrived, the governor had eliminated the budget and I didn't have a job. But I had my camera, and I became a member of the gay press. With my Advocate magazine press pass, I could go anywhere in San Francisco without an invitation. All I had to do was flash that press pass.

In 1978, I went to my first Pride Parade in San Francisco. Thirty artists made flags and every flagpole had a different design. I thought “What a fantastic art installation!” There were three large rainbow flags made by Lynn Segarblom (aka Fairie Rainbow Argyle) and James McNamara. Gilbert Baker served as a co-chair of the Pride flag committee with Lynn. In the years that followed he would promote the rainbow flag as an international symbol of our movement.
I went to the Parade Committee meeting and there was a huge fight between women, artists, people of color, and the white male Parade Co-chair who had invited Ronald Reagan to speak. I photographed this historic meeting where the Committee voted to include women and people of color on the stage. But then the Parade leadership refused to do it.
During the Parade, as a member of the press, I was admitted to the area behind the main stage on the Polk Street steps of City Hall. The lesbian comic, Robin Tyler, and a huge group of women and their supporters rushed forward, pushed through the fence and reached the stage. Meanwhile, the Parade’s security told me I could not photograph what was happening.
I was flabbergasted that I was censored and was so angry I couldn't sleep. The gay press, with the exception of the Bay Times, was misogynist and racist. I had the only photographs of the demonstration. So, I made the editors of the gay papers sign an agreement that they would mention that the Parade Committee ejected me from the press area for taking the pictures. I went to the next parade meeting, and criticized the Committee for failing to support freedom of the press. Somebody made a motion to remove the male co-chair from the parade. Then somebody got up and nominated me. I was so angry that I said OK– and I was elected.
The first motion we made was to change the name of the Pride Parade from “Gay Freedom Day” to “Lesbian/Gay Freedom Day.” Most of the new Parade Committee was made up of artists. My co-chair was Barbara Cameron, a Lakota Sioux whose writing was published in Cherrie Moraga’s This Bridge Called My Back. Then the new committee proceeded to change the rules of the parade to require that every subcommittee had to have a minimum of 50% women. We agreed to make a good faith effort that by 1983, 30% of the committee chairs would be people of color.

Gender Queer performance artist Stephen Varble at the New York Avant Garde Festival, 1975. © Greg Day
We decided to invite Tom Robinson, a popular gay English rock star to participate in the upcoming Parade. His song, “Glad to be Gay!” was very popular. We were worried that the U.S. Immigration Service would stop him at the border. Somebody said, “Call attorney Mary Dunlap,” Mary arrived at the Parade office our office and said “They are violating your constitutional rights as American citizens to have collegiality with people from other countries. You should sue them.” Barbara Cameron and I looked at each other and said “Yes, let's do it!
We had a court date 10 days before the Parade. We sued the U.S. Attorney General and the U.S. Immigration Service and the hearing was held before Judge Aguilar, a Mexican American judge. Mary Dunlap won the case, and for the 10 days prior to the Parade, Northern California was the only place a queer person could enter the United States. We organized a big demonstration at the airport when Tom Robinson entered the country. That was my start in San Francisco politics.
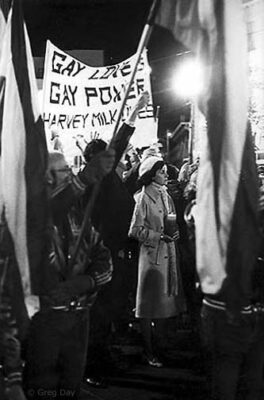
SF Mayor Dianne Feinstein at the Memorial March for slain Supervisor Harvey Milk and Mayor George Moscone, 1979. © Greg Day
At the end of the 1981 Parade, motorcycle police attacked the crowd. We caught it all on video. For the first time Barbara Cameron and I met with Dianne Feinstein, who to her credit, felt her job as Mayor was to meet with everybody. Even though many LGBTQ people didn't like her and thought that she was too old-fashioned and conservative, I appreciated her fearlessness. We argued that we paid the cops’ salaries and they had attacked us. Feinstein had become Mayor because a former police officer had assassinated Mayor George Moscone and Supervisor Harvey Milk. She told us she would work on it. This was my first introduction to Mayor Feinstein and it opened a doorway to local politics.
Soon I became an officer of the Stonewall Democrats. Then Jeff Jones, recruited me to become the Issues Chair of the Alice B. Toklas Lesbian/Gay Democratic Club. The Alice Club in those days was much more radical than it had been before. Mr. Jones was the Treasurer and was also writing grants for artists and arts organizations. The Arts. Randy Stallings was President, Connie O’Connor was the past president, Sal Rosselli was the Vice President.
One of my boyfriends was on the Mayor’s Lesbian/Gay Advisory Committee. One morning, he said to me, “You complain all the time about Dianne and you're getting nowhere. You should be on her Advisory Committee. Maybe she'll listen to and learn from you.” Three days later I started attending the group’s monthly meeting with the Mayor. There were about 40 people, mostly gay male realtors and lawyers and also activists like Pat Norman and Konstantin Berlandt.
Around this time the White Panthers, a group of gun enthusiasts, launched a campaign to recall Mayor Feinstein. Dianne had just vetoed the first Domestic Partners ordinance passed by the Board of Supervisors The White Panthers found a willing group of angry gay people on Castro Street who signed the recall petition.
The Alice B. Toklas Lesbian/Gay Democratic Club was close with Dianne because the Harvey Milk Lesbian/Gay Democratic Club had never supported her until the run-off election of 1979, when the choice was Feinstein or Supervisor Quentin Kopp, the most conservative member of the Board.
Dianne needed the endorsement of the Alice Club, the largest Club in San Francisco’s LGBTQ Community. I was the Chair of the Issues Committee and also on its Executive Committee. The Alice leadership decided to ask for a meeting with the Mayor. Once she accepted, Jeff Jones convinced us to think about what funding items we could ask her to support. Everyone on the Committee had ideas and when the list was put together, each of us took responsibility for asking for one item.
I just want to give you a picture here of the Alice Club’s ability to see the politics of the situation. When we met for lunch with the Mayor at an upstairs private room in a restaurant near City Hall, we asked for everything: money to support AIDS education and prevention campaigns: funding for the recently formed San Francisco AIDS Foundation; support for the Rape Crisis Center; a battered women’s shelter; funding for the Women’s Philharmonic; the Lesbian Rights Project; a contract with a Tenderloin Hotel to serve homeless people with AIDS; support for Community United Against Violence (CUAV). I’m sure I’m forgetting something…
JJ: Yes you are! We asked Dianne to appoint you to the Citizens Advisory Committee of the Community Development Block Grant Program.
GD: Yes. At the meeting, Dianne Feinstein understood that she would have to deliver on at least some of these items to insure the Club's would vote “no” against the recall. To our surprise the Mayor agreed to everything! There was only one exception: she refused to march with Alice in the upcoming Gay Pride Parade. She worried that if she did, 1000 drag queens would dress up as Dianne and march behind her. The Mayor received an unanimous endorsement from Alice.
Soon afterwards the Mayor appointed my boyfriend to the Community Development Committee that recommended how she should allocate San Francisco’s Community Development Block Grant that annually amounted to approximately $26,000,000.
At that time, the only City funds awarded to the LGBTQ community were for mental health, probably because most earlier city officials secretly thought we were mentally ill, if not crazy.
I read in the SF Chronicle that the Housing and Urban Development Department of the Federal Government had asked the Mayor to form a new Citizens Advisory Committee since the one currently in existence had conflicts of interest. This announcement happened two weeks before the annual deadline to appropriate $26,000,000 to the City’s non-profits.
That same day I received a call from Jeff Jones who asked me to talk to my boyfriend who had just been removed from the Citizens Advisory Committee, and get him to recommend me to the Mayor as his replacement. I said, “why would I want to be on that committee?” Jones replied, “That committee hands out $26,000,000 dollars every year and the LGBTQ Community doesn’t get any of it.”
So, I joined this committee of 16 people; 8 men and 8 women. There were 2 straight white people and me, a white queer; the other 13 members were people of color. All of us were newly appointed. The Chair was the head of San Francisco’s NAACP. We had one week to review 400+ applications and recommend how the Mayor should allocate the $26,000,000. It was crazy.
Dianne said the arts were not included in this category and that existing groups should be cut by 10%. Immediately there was a huge fight between the Latino and Black communities. To resolve this problem, we put together a multicultural coalition of the Committee’s Asian, Latino, African American, Native American members. We cut every large group by 5% to fund new programs in under-served communities.
The Committee decided to interview the groups seeking first-time funding. One of them was a consortium of arts groups including the San Francisco Mime Troupe, the S.F. Ethnic Dance Festival, Theatre Rhinoceros, the Women’s Philharmonic and the Lorraine Hansberry Theater. When Marie Acosta of the Mime Troupe was testifying, the only white straight guy on the Committee called her a “Latina bitch.” When the Committee was meeting at 5 o'clock, the same unhinged nutcase started yelling that he would crack my faggot head, I was a “cock-sucking son of a bitch” and that queers were destroying San Francisco.” The guy physically attacked me but was restrained by other Committee members.
At the Committee meeting I said, we won’t get anywhere with this kind of person on our committee and we only have one week. Some woman made a motion asking the Mayor to remove him. I voted for that! Once the meeting was finished, I went home and soon received a phone call from Chuck Forester the Mayor’s gay assistant who asked “Have you talked to the press yet?” I hadn’t. Then Dianne came on the line and said “Oh, this is so terrible. I can't believe this happened.” So I asked her to get rid of the man and replace him with Barbara Cameron. I said, Barbara is a peacemaker and would be its first Native American and first lesbian on this committee. Dianne said “Consider it done.”
But before she hung up, she asked me, “What’s this arts stuff?” Before politics, my life was always in the arts. Not mainstream artists, but women and people of color, as I said earlier, I studied and worked with the Gullah Geechee people and I was a photographer. The arts are where I have always been comfortable. I explained to the Mayor that the Consortium was a coalition of 5 different arts organizations from the African American, Latinx, Asian American, Gay and Women’s communities and the recommended allocation was not a large amount. She said, “All right, just do it!”
GD: I was very polite with Dianne. I talked to her in an empathetic way. When it came time for the vote at Alice, it was really a tempest. We we're meeting in the old Swedish American Hall on Market Street. It was packed. Dianne was there to make her speech. Then we presented the Chair’s Issues Report. I got up and I said, “Dianne has agreed to do the following things, but she has never delivered, and I urge a 30 day wait until she does.” She heard that. It was a spectacle. Over 450 people voted and Dianne won.
JJ: And we walked off with all the money. That was the ironic part!
GD: About 2 months later we had the first meeting of the new fiscal year. It was time to elect the Chair. The current Chair tended to cut women off when they were speaking, and women made up half the committee. He was nominated and then Barbara Cameron nominated me. I looked at her like, you want me to run against the president of the NAACP? All 8 women voted for me and I voted for myself so I became the Chair.
As the Chairman of the Citizens Advisory Committee, I was able to open the door to additional city dollars being directed to the LGBTQ community and having Barbara Cameron on the committee was one of the reasons we succeeded. For example, Barbara advocated for the Women’s Building of the Bay Area, which for some reason the Mayor hated. Barbara and all the other female committee members allocated $400,000 to reduce the Women’s Building’s outstanding mortgage balance.
Let me point out that at that time, Dianne was the first elected female mayor of a major American city. Behind her tough facade was a very empathetic person. She listened and learned something from the community members she interacted with. I remember saying to her, “Dianne, I hope you will remember our runaway and throw-away children who are selling their bodies on Polk Street to survive.” This was how the Larkin Street Youth Center was funded. The gay community’s relationship with Dianne deepened as AIDS spread. She became the leading voice of American cities whose public health systems were being overrun with AIDS patients who had no insurance and no income.
GD: So, Dianne expanded her administration when she ran for reelection to include former opponents and activists from the Alice Club, and many other people. I served on many different committees; the adolescent AIDS advisory committee; the Children's and Families Council. I became the President of Coleman Advocates for Children and Youth, an independent multi-issue advocacy group.
But I want to go back before I leave anything out here. Mr. Jones kept writing grants to the Citizens’ Advisory Committee. Not just for the LGBTQ, but for many underserved communities like the Russian Senior Services, Women Incorporated and the Buddhist Refugee Resettlement Services, a group dealing with the Southeast Asian boat people. He would alert me to the application, and I advocated for them and they got on the docket. I was… what’s it called…?
JJ: …A channel.
GD: Many in the queer community were insulted by Dianne’s attempt to “clean up” San Francisco. She had grown up in a very prosperous family in a Pacific Heights mansion, and her father was a prominent doctor. She went to the Cathedral Girls School, a very posh private school. For some unknown reason, while gays were having sex in every public park in town, she decided to go on the warpath against the Mitchell Brothers, who ran the largest straight adult entertainment sex club in town. In response, the Mitchell Brothers financed an independent sex film that they screened at their venue for the pleasure of their patrons.

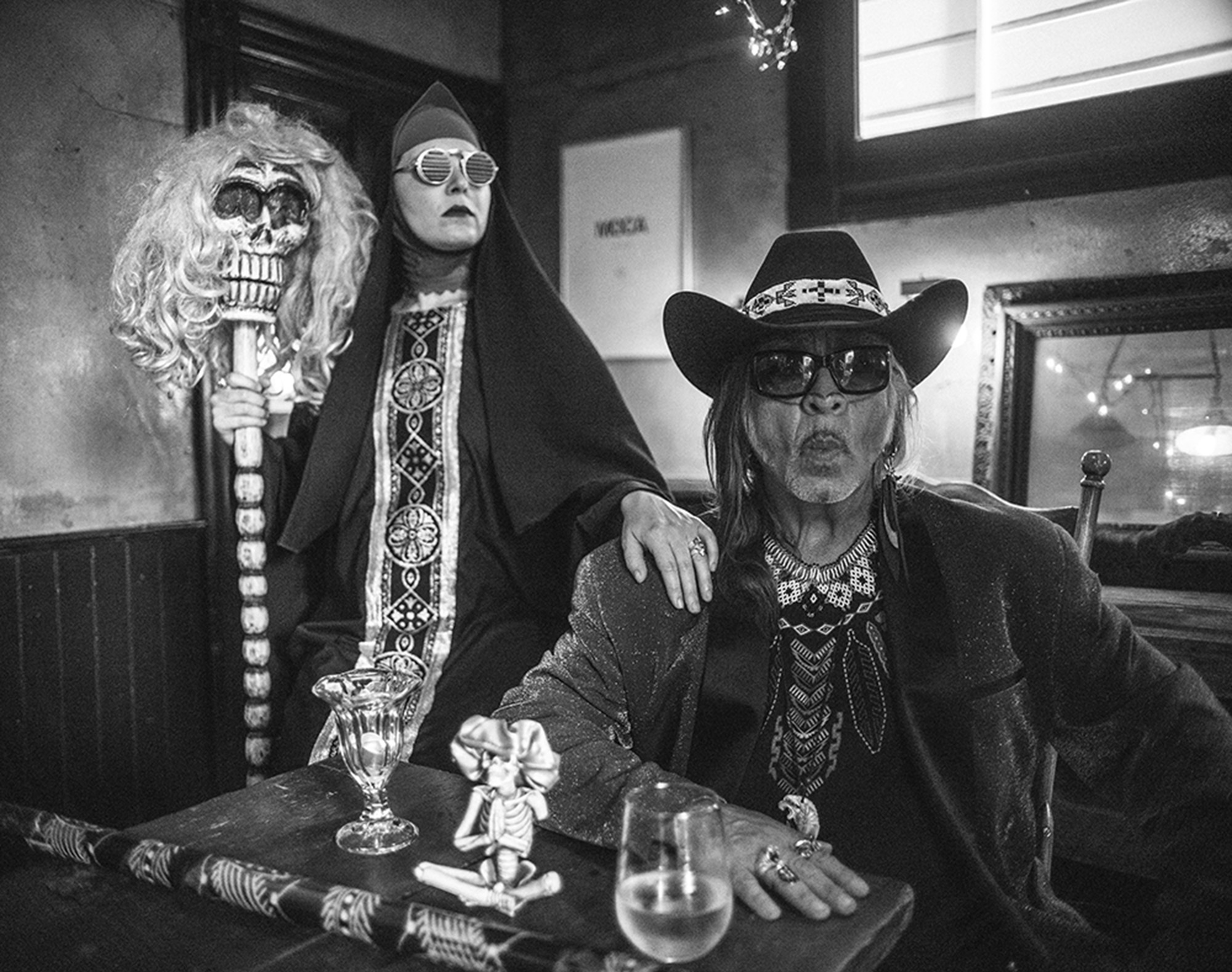
Sisters of Perpetual Indulgence © Greg Day
I went to the event they held to make their case against the city which was attended by a lot of people like Herb Caen, one of the iconic journalists upholding old San Francisco’s reputation. The Mitchell Brothers screened the film. The story was set in their movie theater and there was exact look alike of Dianne Feinstein, and Police Chief Con Murphy sitting in the front row. In uniform, Con Murphy reached into his briefcase and pulled out a dildo shaped like a cable car. The Dianne character spread her legs and as he put it in her vagina, she lit up. While the Mitchel Brothers’ film is showing, in the back of the actual screening room, there was this really loud laugh, and it turned out to be Police Commissioner Jo Daley, Dianne’s appointee. She was drunk as a skunk and was quoted in the Chronicle saying, “That's the funniest thing I've ever seen.”
I'm saying all this because Dianne Feinstein became a national hero. Once a U.S. Senator, she campaigned for gays in the military, and became the leading national voice for all things related to AIDS. Many times, she was the only voice and she stood her ground in supporting LGBTQ rights. Not only that, she provided more funding for AIDS advocacy than any other U.S. elected official. Dianne also became the number one advocate against guns in the country. She introduced and passed a national law outlawing the possession of automatic weapons. This law reduced mass shootings and lasted for 10 years until George Bush let it lapse without a fight.
So what else is on your list here, Jeff?
JJ: Well, there's several other things. But since we’re sitting here with Annie Sprinkle, a goddess of porn, would you talk about your history in the porn industry?
GD: Oh, I would love that. You know, it's so rare to have porn be discussed in the context of queer history unless you’re talking with other sex workers.
Well, when I moved here, I had a job lined up at San Francisco State University but then it fell through. I had to survive. I had my camera, so I became an event and portrait photographer. I also hung out with my artist friends. Early on I got a job photographing the parties at The Trocadero Transfer. These events were really elaborate. They had a designer and they spent lots of money decorating the venue. They hired me because I didn't do hard drugs, only a little marijuana. The previous photographer of their holiday party did not get one image in focus because the owner of the club put so many drugs up his nose. There was a lot of sex at these big events. This was the real Barbary Coast San Francisco. But the club was in Chapter 11.
I had a friend who did photographic stills for porn companies. I got hired to photograph box covers for gay porn. I also had a lot of requests from people to do portraits of them for their online profiles. There was a lot of sex everywhere and I went to a lot of sex parties. I started writing profiles, and then I became a contributing editor to several publications including “Drummer” and “Alternate” magazines. I also worked for “Hot House Video”. It was both a personal and professional pleasure.
But when the AIDS epidemic came along, sex became a danger and the scene became mostly obituaries. I stopped doing my erotic work. Then I was diagnosed with HIV. I joined the very first study in 1983. This is an important part of my history. I am a survivor. One of the few. My reason for survival, I guess, is to tell the story of those who are not here. For a long time, I felt that was my job.
Then I went to work for the Shanti Project as the Community Education Director. Shanti Project is a San Francisco non-profit human resources agency that helped people with AIDS very early on. I was in charge of all the training videos, as well as the monthly newsletter. So all of my photography, even some of my commercial portraits, had an activist agenda. These were images of our community taken from within, an immersive research methodology within anthropology. I had learned from the basket-makers that only the native knows best. As a photographer, I began to allow the subject to direct my shoot. I would give up control. I tried to change the dynamic so that it’s not a photographer and a subject. It’s people talking to each other through the camera. That's what it's all about.
Same with my erotic stuff that I created with my crew of cohorts in San Francisco. It was about presenting a queer aesthetic, a queer viewpoint of life. This aesthetic didn’t exist in our childhoods, or in much of our adult lives.
After my AIDS diagnosis, doctors told me I would have full-blown AIDS within 3 years and that would be it. But then after 3 years, nothing happened. So I decided that I would make as much change as I could in the short time I had left. It turns out the doctors were wrong. I think I am a mutant. About 5% of people of European ancestry have some inherited immunity related to the plagues, like the Black Plague, of the Middle Ages. So I thought, I've got to go back into the BDSM and fetish sex worlds and celebrate the sexuality of the survivors. Many of us who were HIV-positive started celebrating queer sex again, safely.
I got involved in porn. I worked with “Hothouse Video”. My photo models were people I met on the street or in my daily life. In 1995, Rosa Von Praunheim, a celebrated German filmmaker, came to San Francisco to make a documentary about 100 years of queer history. He had a big budget from the “ARTA TV” and a film crew. After his premiere of “Transexual Menace” at the Castro Theater, I asked if he'd been to any San Francisco sex clubs like Blow Buddies. He hadn't, so I said I’d take him there. He said, "We go tonight!"
Rosa had a large film crew and shot 40 hours of video in San Francisco for a 1-hour documentary. A year later, Rosa called from Berlin and said, "Darling, we'll have an exhibit of your photos. Come to Berlin for the Homo 2000 Festival celebrating the 100 birthday of ‘Magnus Hirshfield's Committee on the Science of Sexuality’; we will pay for your flight and accommodations. I will send somebody to the airport to pick you up.”
The show of my photos was at the “Akademie der Kunste”, which has been a Berlin art center for over 300 years. At my opening, Rosa introduced me as a famous world-renowned photographer from San Francisco. There was a huge crowd with lots of press. Rosa gave me a big kiss, and he told the audience, “Darling, your work is about nature. Cocks and trees. It's all about nature.”
In Berlin I spent two weeks staying at Rosa's apartment. When I came back to San Francisco, Tom Ammiano, who was President of the Board of Supervisors, told me he had the same great experience in Berlin. San Francisco felt like a hick town compared to Berlin. This experience made me reevaluate my ideas about art. Berlin opened the door, and the world got bigger and bigger from my European art experience.
In New York, on Thanksgiving weekend in 1995, I met Rick Karp at the Lure leather bar. We hit it off and went back to the hotel where he was staying. The next day he’s putting on his angora sweater and I told him he could be a porn star, he was a natural. A year later, he called me and said, “I'm coming out to San Francisco and I want you to introduce me to the porn industry.”
At the airport Rick didn't look like the same person: He was covered with new tattoos by a famous artist, his hair was cut short and he was buff from working out. Hot House Video hired me immediately to do a shoot of him and they also hired him as the star in his first film. They brought me on the set to serve as a fluffer. It was really a big film. There were over 20 porn stars featured! Cole Tucker (Rick’s stage name) was introduced to the porn world!
After that, I did 2 erotic books, both published in Berlin by Volker Johnson, thanks to Rosa. In these books were landscapes, portraits, fisting, golden showers. bondage, flagellation and oral sex. I asked Volker, “How will you get it past US Customs?” Barnes and Noble ordered the book at a German book fair and placed it in bookstores throughout the US. Because they were published in Europe and had tasteful covers, it was seen as art and that is how the books got through customs.
In 2000 my mother, who had moved to San Francisco to be near me, had a stroke that left her unable to walk She was in assisted living which was the only place I could house her. She wasn’t happy. Eventually I asked my friend, Jeff Jones what he would do in my position. He said, “you are spending over $30,000 a year on rent and both of you are unhappy. Your mother and you should buy a house in Palm Springs and you should move there. Then your mother can live out her days and you will own a house.” My mother loved everything about this idea. She was thrilled. So that’s what we did.
Some friends of mine from San Francisco had moved to Palm Springs to retire. They invited me down. It was winter with snow on the mountains and absolutely gorgeous. At the time that I left San Francisco, the dot.com bust was about to happen. The entire United States still has remnants of this diaspora of evicted San Franciscans.
My porn star buddy Rick was working as a realtor at Coldwell Banker in Palm Springs. On the first day of our search, I found the house I wanted and bought it. It was all serendipitous. My mother lived the last 5 years of her life with me in Palm Springs and it was a gift to both of us.
JJ: Okay, now I want to talk to you about the Queer Cultural Center (QCC), which you were a founder of. What do you think the impact of the Queer Cultural Center has been?
GD: Each of us who founded the QCC had a desire to present our art as a portrait of our community’s diversity, whether we were a person of color, a woman, or a white cis man.
JJ: When I wrote my first report about the boards and staff of the major arts institutions, you said to me, “Well, what about the queers?” So when I did my follow up study on arts funding at Grants For The Arts (GFTA) I compiled the statistics for people of color, women and queers.
GD: At the time, the mid-1980s, the City’s queer community was primarily white and male. People of color and lesbians were increasingly moving to the East Bay. White Gay men were the demographic majority in San Francisco’s LGBTQ community. The queer community struggled to include women and people of color. Creating the Queer Cultural Center was our dream.
QCC’s by-laws required that the majority of our board were women and people of color. We didn't just add more activists, we added brokers, and artists who were activists for cultural equity. It was fun to be part of this. Putting the National Queer Arts Festival together and making it balanced and equitable, was a labor-intensive job. Every one of us was involved. Ours was a working board.
JJ: Yeah, because we had no money. Not yet. The first grant that Queer Cultural Center got was from the California Arts Council’s Multicultural Advancement Program. They were awarding 30 grants of $2,000 a year for 3 years. The program’s Director, a straight Latina, said to me, “If people of color are the majority of your board, QCC is eligible to apply and you should.” We had originally inserted this particular language into our by-laws to give our organization credibility with the increasing number of people of color who were entering the philanthropic field. They were not sure they wanted to fund queers. But if you have a majority of queer people of color on your board, then they perceive your organization in a different way.
When we interviewed Pam Peniston, an African American lesbian, for the position of Artistic Director we were talking about the alliance-building that happened with the Community Development Block Grant Consortium (CDBG) of 1983. We succeeded because we built alliances with people of color. The first CDBG Consortium included Quentin Easter who was queer and African American, Elizabeth Min who was a queer Asian, Marie Acosta a mixed-race Latina/Native American, Alan Estes, a queer white man and Bruce Davis, the straight white Director of the Ethnic Dance Festival. We operated as a multi-racial lobby group; we sent selected combinations of people capable of addressing the interests of each Supervisor.
GD: We found some of the most talented, capable people in these communities. For a long time, I was totally enthralled by black women artists and their influence on me was huge.
JJ: Remember Adrienne Fuzee, the black dyke curator who was one of the original Board members of QCC and who died soon after we started QCC?
GD: Yeah, I loved her. Every government agency, every arts organization has to find a person like her; a queer person of color with a strong artistic vision.
JJ: That's why Pam Peniston was the artistic director of QCC. Whenever her position was threatened, I stood by her at all costs. She was the key to our funding. She was the face of QCC and she enabled us to secure any number of grants. By 2010, QCC was one of the first LGBTQ arts organization to be funded by the National Endowment for the Arts. One of Pam’s artist friends started working at the Hewlett Foundation, and suddenly QCC was funded there as well.
GD: But you know, I have not seen Annie and Beth’s live performances but I would love to see them sometime.
B&A: We’ll have to do something in Palm Springs. We're doing work about loving the Earth, environmental justice and ecosexuality. These days we are Fluxus-inspired, queer environmental activists. We are curious about preserving your archive. Has your archive been placed yet? Where?
GD: I have such a huge archive that it's going to go to several different places. I'm working on that. I don't have a place for my erotic work except for the Leather Archive in Chicago and possibly the “One Archives” in Los Angeles. I had an exhibit recently at LA’s One Gallery. I am also negotiating with Atlanta’s High Museum about purchasing my collection of baskets and photographs of the Gullah communities of the Sea Islands taken in the early 1970s.
Annie: We have so much in common that I'm surprised we haven't met before. I lived in lower Manhattan in the 70s to early 90s. I was also briefly a fluffer! I had sex on the piers. I also went to gay men’s orgy bars at the Mineshaft, the Tryst and the Toilet. I had quite the leather wardrobe. I am a photographer too. I majored in photography at the School of Visual Arts in Manhattan. I shot for all the sex magazines, including gay men's magazines. I was the woman who shot straight men for gay men.
GD: New York, in ‘75 or ‘76, was wild and radical, but still you could be sent to Rikers Island or be given a lobotomy if you practiced queer sex. We were still living under archaic laws. In 1976, I visited a boyfriend who retired from the U.S. Navy and went home to San Francisco. I learned that being gay was not only legal in San Francisco, but it was also important. To anybody living in the rest of America, regardless of your background, this was a shock. So I thought I have to get to San Francisco.
Most of us couldn't come out in our hometown or to our family, because we would have lost our jobs or our children. We could have been listed on a police profile. People moved from small towns to New York or Chicago. In the seventies, and there was a huge move from the East Coast to San Francisco and California. Ever since the Gold Rush, almost 150 years ago, San Francisco has thought of itself as the most important place in the world, when it is really just a village. You could put San Francisco in one neighborhood in Los Angeles. San Francisco is so incestuous and introverted that it believes it has invented everything and that, of course, is not true.
After the recession in 2008, I moved into West Hollywood and then East Hollywood for 12 years. In one month in LA, I met my partner of 15 years, Gordon Pollack, a fellow artist.
Mr. Jones created a following of art groupies, who worked collectively. Jeff created the California LGBTQ Arts Alliance, a statewide network of non-profit arts orgs and individual artists. The grant was challenged by artists in Southern California for under representation. As a former QCC Board Member living in Southern CA they signed me up to expand the original network. Mr. Jones said to me “I'm sure there are some other queer arts groups in LA. Let’s sign them up to create a network.” But in L.A. there are 7 queer choruses and an orchestra and all women's groups. L.A. had Harry Hay and the radical faeries, and the Mattachine Society before anything happened in San Francisco.
JJ: The Daughters of Bilitis founded by Del Martin and Phyllis Lyon preceded them.
GD: Los Angeles built queers into their economy from the start, because art is the number one business there-- a trillion-dollar industry. The art industry of LA has 5 times the economy of the Bay Area, including San Francisco. In one year I recruited 35 different organizations into the statewide queer Arts Alliance, funded by the California Arts Council. Nobody had connected them before. So they all said “sign us up.”
The Fowler Museum’s publicity person there was a very talented young woman who joined. The Hammer Museum joined. The Autry National Museum of the West joined. I discovered that Queers ran many of these organizations and served as the publicity and development directors of the Getty and many others. No one in LA ever said “no” to me. But in San Francisco, that's the first word out of their mouth. We'll have to think about it, the committee didn't give you a high enough score, we don’t know if you qualify. It’s business.
I have to admit that Mr. Jones educated me about the power of money. He had a theory about LA funding. The Alliance held a series of public meetings, one at “Highways”, one at the “Macha Theater” in West Hollywood, a lesbian theater company. People came and listened, but they didn't say anything, because they thought that they were already in the pipeline, but they were not. There still was no cultural equity. I retired as director of the statewide Alliance five years ago. Dante Alencastre, a film maker documenting trans gender activism, became the new director.
LA County adopted an ordinance about cultural equity that they learned about from San Francisco. Now cultural equity is required by the City and the County of Los Angeles. Los Angeles County has a 5-member Board of Supervisors and each of them has twice as many constituents than a US congressperson. The decisions they make affect everything in the country. Talk about cultural diversity. There are entire cities of Nigerians, suburbs of Ethiopians or Koreans. It's just like really off the chart. There’s nothing like it. The Bay Area is tiny in comparison. People get the arts in LA. There's money. Money and work.
B&A: Thank you for all you have done for queer arts, Greg.
JJ: You've been a very entertaining interview subject. I didn't have to say much. I could just let you talk. That's what my mentor Carlos Villa taught me. “Just let them talk!”





 B&A: We are also concerned that the people who made this arts funding history started dying before this history has been documented or preserved. So we are creating this archive as a historical record. With all the push-back against diversity, equity and inclusion (DEI), we think it's important for artists, elected officials, educators and community leaders to be able to say, “Hey, they did this in San Francisco. Maybe we can do it here too.”
B&A: We are also concerned that the people who made this arts funding history started dying before this history has been documented or preserved. So we are creating this archive as a historical record. With all the push-back against diversity, equity and inclusion (DEI), we think it's important for artists, elected officials, educators and community leaders to be able to say, “Hey, they did this in San Francisco. Maybe we can do it here too.” When Wallflower broke up and evolved into the Dance Brigade, Krissy Keefer and Nina Fichter hired Sara to make new work with them, and I got to be Sara’s assistant. They were the very first people in the local dance community to embrace Contraband. They brought us into Furious Feet: The Dance Festival for Social Change that they organized in the 80s and 90s.
When Wallflower broke up and evolved into the Dance Brigade, Krissy Keefer and Nina Fichter hired Sara to make new work with them, and I got to be Sara’s assistant. They were the very first people in the local dance community to embrace Contraband. They brought us into Furious Feet: The Dance Festival for Social Change that they organized in the 80s and 90s. Anyways, many of the artists who were attracted to Sara were very politically engaged. Kim Epifano came out of the Dance Brigade. I came out of different anarchist scenes. Nina Hart was also very involved in anarchist and feminist politics. I was obviously queer from the late 80s onwards, and was extremely involved in ACT UP and Queer Nation; both crucial to the queeruption aka cultural and political uprisings in response to AIDS.
Anyways, many of the artists who were attracted to Sara were very politically engaged. Kim Epifano came out of the Dance Brigade. I came out of different anarchist scenes. Nina Hart was also very involved in anarchist and feminist politics. I was obviously queer from the late 80s onwards, and was extremely involved in ACT UP and Queer Nation; both crucial to the queeruption aka cultural and political uprisings in response to AIDS. JJ: Yes, it feels to me like we are back to where the arts world was in the mid-1980s, when we had words like “multiculturalism” and nobody knew what it meant. The California Arts Council is a really great example. They have a so-called “peer review” process, but it’s not the peer review system of 40 years ago that was facilitated by specialists in the arts discipline, who knew the significant artists and organizations and who was empowered to interrupt and correct any mis-statements of facts made by the panelists.
JJ: Yes, it feels to me like we are back to where the arts world was in the mid-1980s, when we had words like “multiculturalism” and nobody knew what it meant. The California Arts Council is a really great example. They have a so-called “peer review” process, but it’s not the peer review system of 40 years ago that was facilitated by specialists in the arts discipline, who knew the significant artists and organizations and who was empowered to interrupt and correct any mis-statements of facts made by the panelists. B&A: She became the brilliant Executive Director at CounterPULSE.
B&A: She became the brilliant Executive Director at CounterPULSE.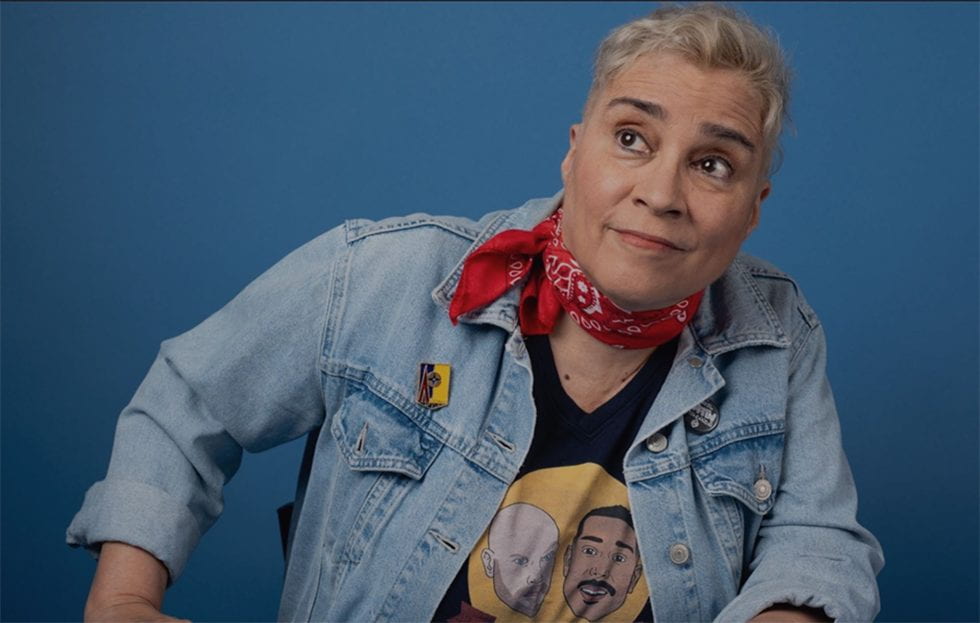
 JJ: Marga: When did you move to San Francisco?
JJ: Marga: When did you move to San Francisco? My touring performances in Europe were the first time that I actually earned money as an entertainer. I worked with Lilith on and off. I think I went on a second European tour with them in 1981; then I came back to my job making omelets at the Acme. There was a publication back then, called Backstage I think, where you could find out about auditions. I auditioned for Les Nickelettes and worked with them on a couple of shows. That was basically my life from 1976 to 1982.
My touring performances in Europe were the first time that I actually earned money as an entertainer. I worked with Lilith on and off. I think I went on a second European tour with them in 1981; then I came back to my job making omelets at the Acme. There was a publication back then, called Backstage I think, where you could find out about auditions. I auditioned for Les Nickelettes and worked with them on a couple of shows. That was basically my life from 1976 to 1982.
 I appeared in a Mime Troupe show called Crossing Borders. It was about Salvadoran immigrants and what they were going through. I went on tour with that show. That's where I met Stacy Powers-Cuellar, who now runs Brava Theater. Maria Acosta played my sister in the show, or a cousin or something. It was a great experience to work with them. But I didn't really have the chops, to be honest.
I appeared in a Mime Troupe show called Crossing Borders. It was about Salvadoran immigrants and what they were going through. I went on tour with that show. That's where I met Stacy Powers-Cuellar, who now runs Brava Theater. Maria Acosta played my sister in the show, or a cousin or something. It was a great experience to work with them. But I didn't really have the chops, to be honest.
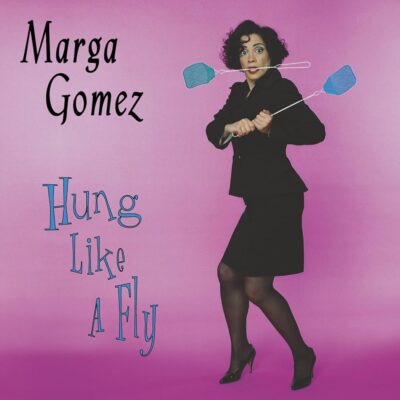 MG: That's right. Tim Miller. Holly Hughes, Annie Sprinkle, my show Memory Tricks, which all got a lot of press attention. I was invited to be in the Sundance Writer's Lab. It was the first time that Sundance invited playwrights. We would tell the filmmakers our play, our story, then talk about adapting it to a film. One night 5 of us soloists each did our shows on stage and everyone in the audience was a filmmaker. This really taught me the power of the solo art form.
MG: That's right. Tim Miller. Holly Hughes, Annie Sprinkle, my show Memory Tricks, which all got a lot of press attention. I was invited to be in the Sundance Writer's Lab. It was the first time that Sundance invited playwrights. We would tell the filmmakers our play, our story, then talk about adapting it to a film. One night 5 of us soloists each did our shows on stage and everyone in the audience was a filmmaker. This really taught me the power of the solo art form.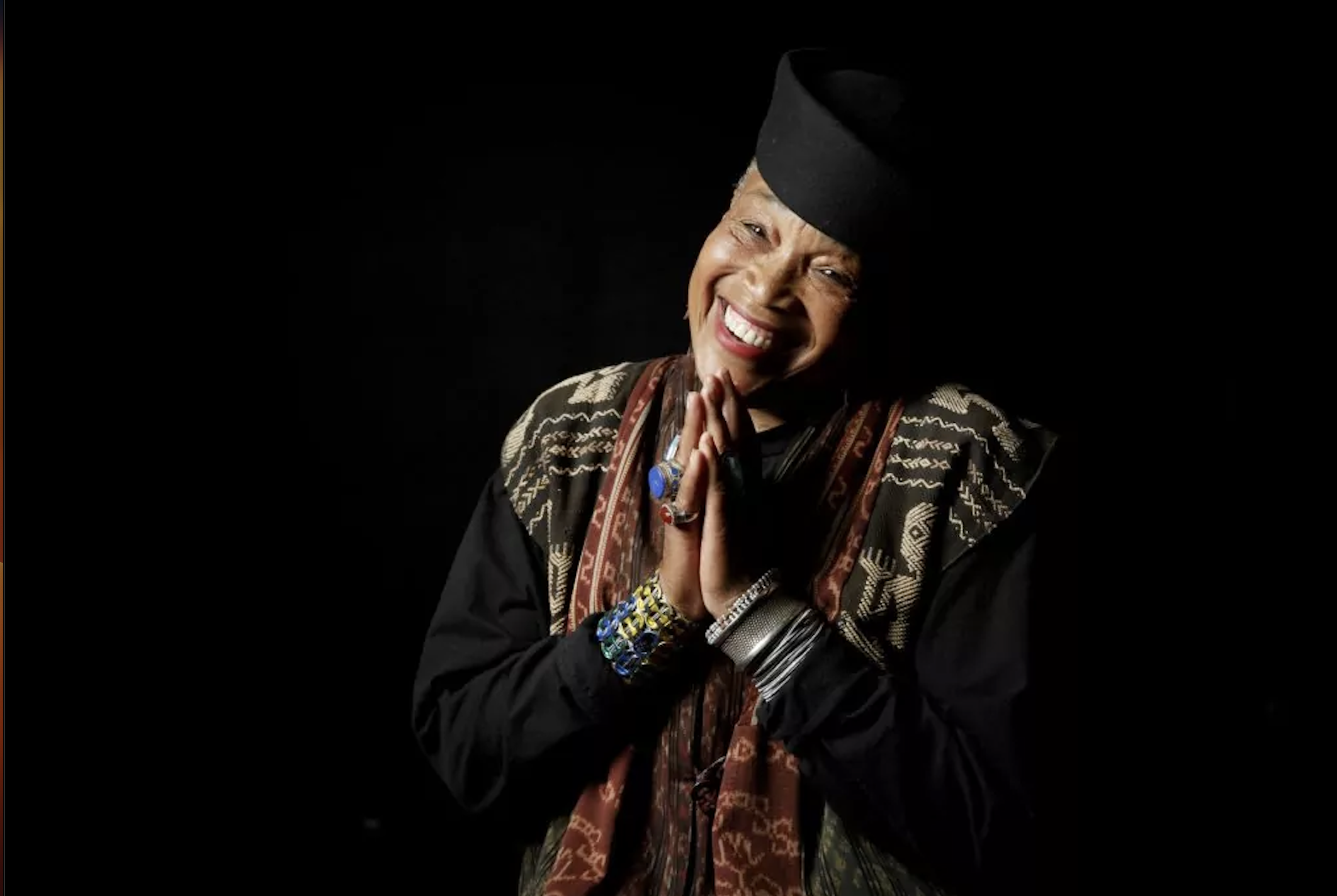
 B&A: When did you get involved with Idris Ackamoor and Cultural Odyssey?
B&A: When did you get involved with Idris Ackamoor and Cultural Odyssey? I remember being in Berlin with Cecil Brown, the writer. I was doing some nude work in Berlin and this crazy woman came to the club. She was taking us over to her house for dinner, but then she pulled out a gun. Cecil said, “Whoa, what the hell?” And she said, “Do YOU have a gun?” I think the goddamn gun went off.
I remember being in Berlin with Cecil Brown, the writer. I was doing some nude work in Berlin and this crazy woman came to the club. She was taking us over to her house for dinner, but then she pulled out a gun. Cecil said, “Whoa, what the hell?” And she said, “Do YOU have a gun?” I think the goddamn gun went off. RJ: Well, The California Arts Council awarded the Sheriff’s Department a grant to hire me as a resident artist in the Women’s jail. My job was to go into the jails and teach aerobics to incarcerated women. Looking back, I realize that they just didn't know what else to do with all of these women in jail.
RJ: Well, The California Arts Council awarded the Sheriff’s Department a grant to hire me as a resident artist in the Women’s jail. My job was to go into the jails and teach aerobics to incarcerated women. Looking back, I realize that they just didn't know what else to do with all of these women in jail. JJ: The first Medea Project production was Reality is just Outside the Window. Your solo show Big Butt Girls, Hard-headed Women was also about incarcerated women. You were doing something very different than everyone else in the theater world. Medea wasn’t just a solo performance. It was a reality-based performance featuring both professional actors and prisoners. The weird thing was that the audience couldn't always tell who was a prisoner and who was a professional actor.
JJ: The first Medea Project production was Reality is just Outside the Window. Your solo show Big Butt Girls, Hard-headed Women was also about incarcerated women. You were doing something very different than everyone else in the theater world. Medea wasn’t just a solo performance. It was a reality-based performance featuring both professional actors and prisoners. The weird thing was that the audience couldn't always tell who was a prisoner and who was a professional actor. B&A: When is that piece going to be up, Rhodessa?
B&A: When is that piece going to be up, Rhodessa?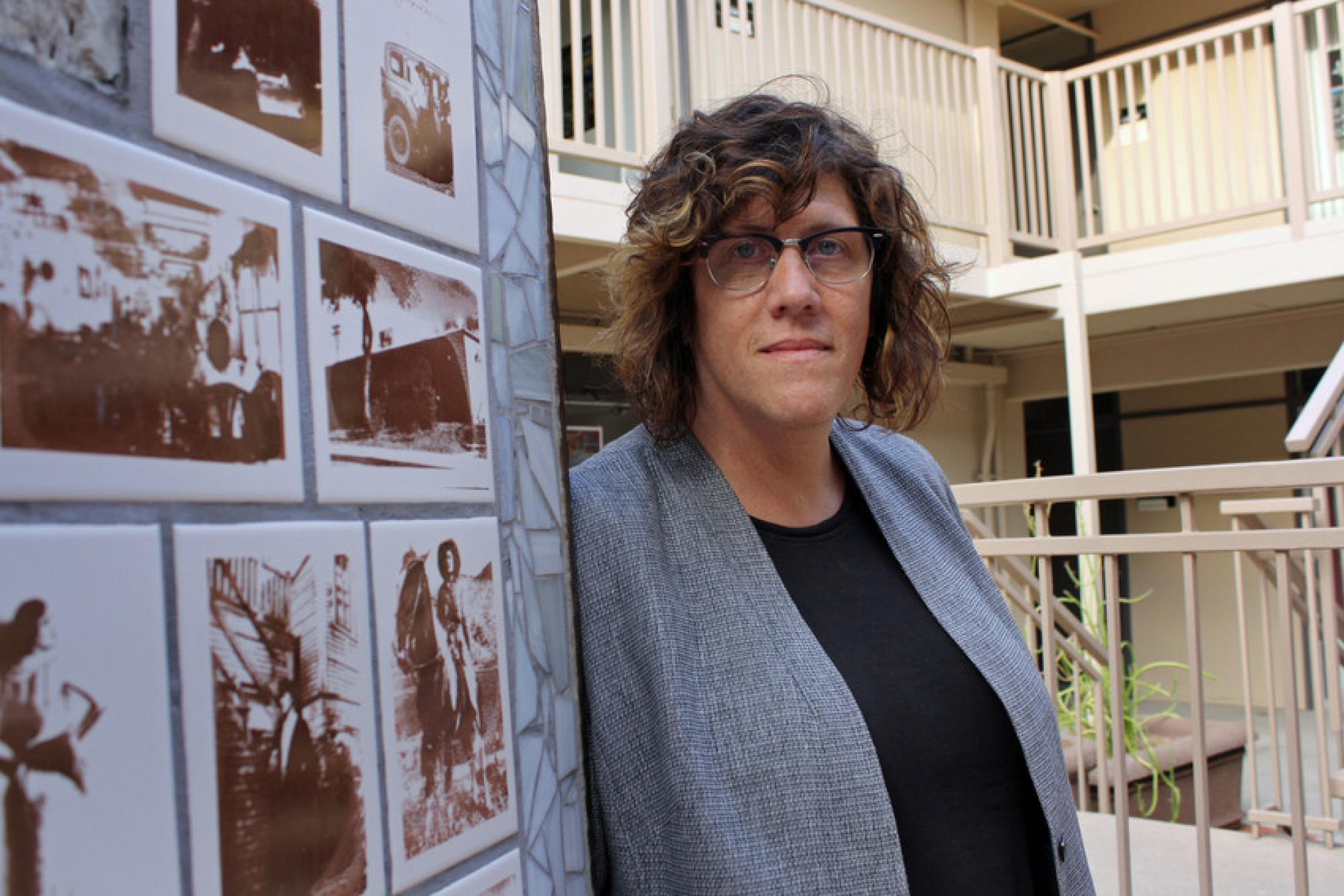
 JJ: What year did you become the director of the GLBT Historical Society?
JJ: What year did you become the director of the GLBT Historical Society? B&A: According to Wikipedia, Tranny Fest became the San Francisco Transgender Film Festival, and it was the world’s first trans Film Festival. And we were there! Memories are full.
B&A: According to Wikipedia, Tranny Fest became the San Francisco Transgender Film Festival, and it was the world’s first trans Film Festival. And we were there! Memories are full.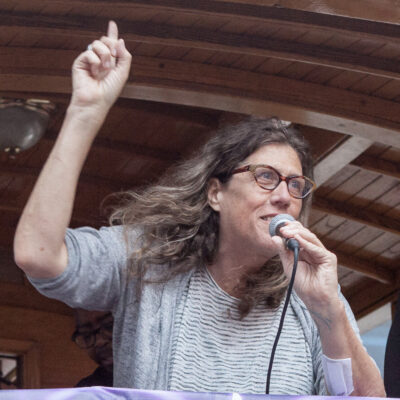 The wave of trans activism that started in the ‘90s in San Francisco, and later fueled a wave of cultural production, came out of that sensibility. It was a way of meeting the moment with regard to the impact of AIDS—trans women of color engaged in survival sex work had the highest infection rates of any demographic—as well as contesting the historic relationship between trans life and an often transphobic cis-gay and cis-lesbian community.
The wave of trans activism that started in the ‘90s in San Francisco, and later fueled a wave of cultural production, came out of that sensibility. It was a way of meeting the moment with regard to the impact of AIDS—trans women of color engaged in survival sex work had the highest infection rates of any demographic—as well as contesting the historic relationship between trans life and an often transphobic cis-gay and cis-lesbian community. I’m thinking, too, of someone like Jayne County, once a drag queen from the South who hustled her way up to New York City doing sex work, became part of Charles Ludlam’s Theater of the Ridiculous, and became a major punk icon with her band Wayne County and the Electric Chairs before she transitioned. They had this amazing song called If You Don't Want to Fuck Me, Baby, Then Baby, Fuck Off. She brought this total, in-your-face punk sensibility to the work that she was doing. She titled her autobiography Man Enough to Be a Woman. She became a fixture at Max's Kansas City, and her style influenced everybody from the Dolls to Bowie to Lou Reed to Blondie. She was an incredibly seminal cultural figure. Is that “trans art” now? I think so. By the time the 1990s rolled around, a late-career Jayne County put out an album called Transgender Rock and Roll. And she paints. She has a really interesting outsider-artist style.
I’m thinking, too, of someone like Jayne County, once a drag queen from the South who hustled her way up to New York City doing sex work, became part of Charles Ludlam’s Theater of the Ridiculous, and became a major punk icon with her band Wayne County and the Electric Chairs before she transitioned. They had this amazing song called If You Don't Want to Fuck Me, Baby, Then Baby, Fuck Off. She brought this total, in-your-face punk sensibility to the work that she was doing. She titled her autobiography Man Enough to Be a Woman. She became a fixture at Max's Kansas City, and her style influenced everybody from the Dolls to Bowie to Lou Reed to Blondie. She was an incredibly seminal cultural figure. Is that “trans art” now? I think so. By the time the 1990s rolled around, a late-career Jayne County put out an album called Transgender Rock and Roll. And she paints. She has a really interesting outsider-artist style.















 JJ: So when you started Wallflower, did you perceive what you were doing as performance art?
JJ: So when you started Wallflower, did you perceive what you were doing as performance art? KK: When Wallflower moved from Eugene, Oregon to Boston in 1981, we had been touring all over the United States, in Europe and Latin America and our work occupied the intersection where lesbian feminism meets solidarity work, exemplified by Chile’s Pinochet and many other US-propped up dictators across the globe. Lesbians were at the center of most solidarity groups supporting the liberation of Nicaragua and El Salvador. Our work married these two struggles on stage and there was an audience for it wherever we went.
KK: When Wallflower moved from Eugene, Oregon to Boston in 1981, we had been touring all over the United States, in Europe and Latin America and our work occupied the intersection where lesbian feminism meets solidarity work, exemplified by Chile’s Pinochet and many other US-propped up dictators across the globe. Lesbians were at the center of most solidarity groups supporting the liberation of Nicaragua and El Salvador. Our work married these two struggles on stage and there was an audience for it wherever we went.  JJ: I think some of these earlier pieces and events you were producing resonated. What about Furious Feet?
JJ: I think some of these earlier pieces and events you were producing resonated. What about Furious Feet? KK: I feel like in dance everybody works with everybody. All the dancers move through many different choreographers because nobody can afford to pay a company except for the ballet, Michael Smuin, Alonzo King and Sean Dorsey. But most dancers move back and forth.
KK: I feel like in dance everybody works with everybody. All the dancers move through many different choreographers because nobody can afford to pay a company except for the ballet, Michael Smuin, Alonzo King and Sean Dorsey. But most dancers move back and forth. KK: I think definitely The Wallflower Order. Creating that collective was the beginning. I think creating the GRRRl Brigade too. Besides that, I think starting the Lesbian and Gay Dance Festival and the first Festival presenting sky dancers– “Women who Fly through the Air.”
KK: I think definitely The Wallflower Order. Creating that collective was the beginning. I think creating the GRRRl Brigade too. Besides that, I think starting the Lesbian and Gay Dance Festival and the first Festival presenting sky dancers– “Women who Fly through the Air.” KK: You got demonized super bad. I remember when someone came to meet with me—she had just been assigned by the NEA to be Dance Brigade’s Advancement Consultant. They told me “You gotta stop working with Jeff.” I didn't understand what was going on. But I do remember looking at a finished grant that just sat on the floor of the closet because you had written it. It was that you were calling Kary Schulman’s Agency (Grants for the Arts) racist and they were all coming after you.
KK: You got demonized super bad. I remember when someone came to meet with me—she had just been assigned by the NEA to be Dance Brigade’s Advancement Consultant. They told me “You gotta stop working with Jeff.” I didn't understand what was going on. But I do remember looking at a finished grant that just sat on the floor of the closet because you had written it. It was that you were calling Kary Schulman’s Agency (Grants for the Arts) racist and they were all coming after you.

